# 代理(proxy)
什么是代理?
这个问题?有点抽象,没有经历的难以理解代理是什么玩意呢?
举一个例子:在我们的生活中,处处有代理的身影案例,就如:我想去租一个房子,我可自己去app上找房源。这中亲力亲为的事情就不是代理了。
我自己去找房子有点麻烦,不知道自己找的房源靠不靠谱哦!那就的去找个代理人(你信赖的人)去帮你找房源,帮你确定可靠的房子。这就是代理。
重要概念
我【被代理对象】
代理人【我找的代理,帮我去干事情的人】
# 静态代理(static proxy)
在java中看看自己找房的代码实现。定义一个上层的接口!【开闭原则】
/**
* 接口:租房
*/
public interface IRentingHouse {
/**
* 找房行为方法
*/
void rentHosue();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
代理人、我。都有一个共同的行为,那就是找房。接口【interface】的定义就是:接口主要对行为进行抽象,没有具体的存在啊!
接下来实现这个接口的类,重写了具体的rentHosue()方法。
实现找房子的接口。
public class RentingHouseImpl implements IRentingHouse {
@Override
public void rentHosue() {
System.out.println("我要租用一室一厅的房子");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
client端测试!
- 自己找房子,创建一个找房子的对象
- 找房子的对象调用方法,执行去找房子(怎么找我们不具体实现,打印输出就行......)
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IRentingHouse rentingHouse = new RentingHouseImpl();
// 自己要租用一个一室一厅的房子
rentingHouse.rentHosue();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
结果:
# JDk动态代理
loader – the class loader to define the proxy class
定义代理类的类加载器
interfaces – the list of interfaces for the proxy class to implement
代理类要实现的接口列表
h – the invocation handler to dispatch method invocations to
将方法调用分派到的调用处理程序
# 1)创建代理人接口
接口:是抽象的开始。
我要找什么样的代理人呢?是性感的秘书小姐姐还是......
所有要定义接口进行抽象化,具体找什么样的,接口我我一顿操作猛如虎定义如下类型:
- 帅小伙
- 性感秘书小姐姐
- 中年小伙
- 等....
以上类型都定义在接口里面....,类实现可以选择一个实现。
下面就不定义这么多类型了,直接全部统称为person吧,行为统一一个方法!doSomething()
创建代理人接口:
package com.gun.dynamicproxy;
public interface Person {
// 统一行为做什么....事情
public void doSomething();
}
2
3
4
5
6
# 2)创建实现代理人接口的类
package com.gun.dynamicproxy;
public class Bob implements Person {
@Override
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("Bob doing Something");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 3)创建代理类
package com.gun.dynamicproxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class JDKDynamicProxy {
// 声明 被代理的对象
private Person person;
//构造函数
public JDKDynamicProxy(Person person) {
this.person = person;
}
//获取代理对象,俗话说:就是找个秘书帮你去干活。
public Object getTarget(){
// person 是属性,要有初始化的一个过程
// 1、构造方法
// 2、set方法
// 3、反射
//帮谁代理:person.getClass().getClassLoader()
// new Handler(person) 处理器类,要实现接口 InvocationHandler
// 写this ,这个类要实现InvocationHandler 接口,重写方法 invoke
// JDk 动态代理是帮我们创建一个代理对象
// 1、类加载器sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
// 2、 person.getClass().getInterfaces() [Ljava.lang.Class;@1540e19d
Object proxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(
person.getClass().getClassLoader(),
person.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new Handler(person)
);// 初始化代理对象实例化。
return proxyInstance;
}
// 如果:将这个方法写到一个类中去了
// 当前代理类就不要实现:InvocationHandler 这个接口
// @Override
// public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// System.out.println("对原方法进行了前置增强");
// //原方法执行
// Object invoke = method.invoke(person, args);
// System.out.println("对原方法进行了后置增强");
// return invoke;
// }
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
InvocationHandler接口是什么:有什么作用?为什么要实现它呢?
package java.lang.reflect;
/**
* {@code InvocationHandler} is the interface implemented by
* the <i>invocation handler</i> of a proxy instance.
是代理实例的 调用处理程序 实现的接口。
*
* <p>Each proxy instance has an associated invocation handler.
每个代理实例都有一个关联的 调用处理程序【要增强的逻辑代码】。
* When a method is invoked on a proxy instance, the method
* invocation is encoded and dispatched to the {@code invoke}
* method of its invocation handler.
当在代理实例上 调用方法时,方法调用将 被 编码并调度到 其调用处理程序的{@code invoke}方法。
*
* @author Peter Jones
* @see Proxy
* @since 1.3
*/
public interface InvocationHandler {
/**
Processes a method invocation on a proxy instance and returns the result.
处理代理实例上 的方法调用并 返回结果。
This method will be invoked on an invocation handlerwhen a method is invoked on a proxy instance that it isassociated with.
@param
# 参数1
proxy the proxy instance that the method was invoked on
proxy方法调用的 代理实例【我们创建的代理对象Bob 是person类型】
@param
# 参数2
method the {@code Method} instance corresponding to
the interface method invoked on the proxy instance.
方法对应于在 代理实例上 调用的 接口方法的{@code method}实例。
The declaring class of the {@code Method} object will be the interface that
the method was declared in, which may be a superinterface of the
proxy interface that the proxy class inherits the method through.
{@code Method}对象的声明类将是在其中声明该方法的接口,该接口可能是代理类通过其继承该方法的代理接口的超接口。
@param
# 参数3
args an array of objects containing the values of the
arguments passed in the method invocation on the proxy instance,
or {@code null} if interface method takes no arguments.
args一个对象数组,包含在 代理实例上的方法 调用 中传递的 参数的值[the values of the
arguments];如果接口方法不带参数,则为{@code-null}。
Arguments of primitive types[基本类型] are wrapped in instances of the
appropriate primitive wrapper class,
such as例如:
{@code java.lang.Integer} or {@code java.lang.Boolean}.
基元类型的参数被包装在适当的基元包装类的实例中,例如{@codejava.lang.Integer}或{@code java.lang.Boolean}。
@return
the value to return from the method invocation on the proxy instance.
从代理实例上的方法调用 返回的值。
If the declared return type of the interface method is a primitive type, then the value returned by this method must be an instance of the corresponding primitive
wrapper class; otherwise, it must be a type assignable to the declared return type.
如果接口方法声明的返回类型是基元类型,则此方法返回的值必须是相应基元包装类的实例;否则,它必须是可分配给声明的返回类型的类型。
If the value returned by this method is {@code null} and the interface method's return type is primitive, then a {@code NullPointerException} will be thrown by the method invocation on the proxy instance.
and 表示并列关系
如果此方法返回的值为{@code null},并且接口方法的返回类型为基本类型,则代理实例上的方法调用将抛出{@codeNullPointerException}。
If the value returned by this method is otherwise not compatible with the interface method's declared return type as described above,a {@code ClassCastException} will be thrown by the method invocation on the proxy instance.
如果此方法返回的值与如上所述接口方法声明的返回类型不兼容,则代理实例上的方法调用将抛出{@code ClassCastException}。
@see UndeclaredThrowableException
*/
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
@throws Throwable the exception to throw from the method invocation on the proxy instance. The exception's type must be assignable either to any of the exception types declared in the {@code throws} clause of the interface method or to theunchecked exception types {@code java.lang.RuntimeException} or {@code java.lang.Error}. If a checked exception is thrown by this method that is not assignable to any of the exception types declared in the {@code throws} clause of the interface method, then an {@link UndeclaredThrowableException} containing the exception that was thrown by this method will be thrown by the method invocation on the proxy instance.
@throws可抛出要从代理实例上的方法调用中 抛出的异常。
异常的类型必须可分配给接口方法的{@code throws}子句中声明的任何异常类型,或分配给未选中的异常类型{@codejava.lang.RuntimeException}或{@cODEjava.lang.Error}方法,
则包含此方法引发的异常的{@linkUndeclaredThrowableException}将由代理实例上的方法调用引发。
# 4)实现InvocationHandler接口
package com.gun.dynamicproxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author liyupeng
* @date 2023/7/13&11:13
* @packageName com.gun.dynamicproxy
*/
public class Handler implements InvocationHandler {
// 声明 被代理的对象
private Person person;
public Handler(Person person) {
this.person = person;
}
// 增强的逻辑是写在这个方法里面的。
// Object proxy proxy方法调用的 代理实例
// Object[] args 原方法的 参数列表
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("对原方法进行了前置增强");
//原方法执行
Object invoke = method.invoke(person, args);
System.out.println("对原方法进行了后置增强");
return invoke;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
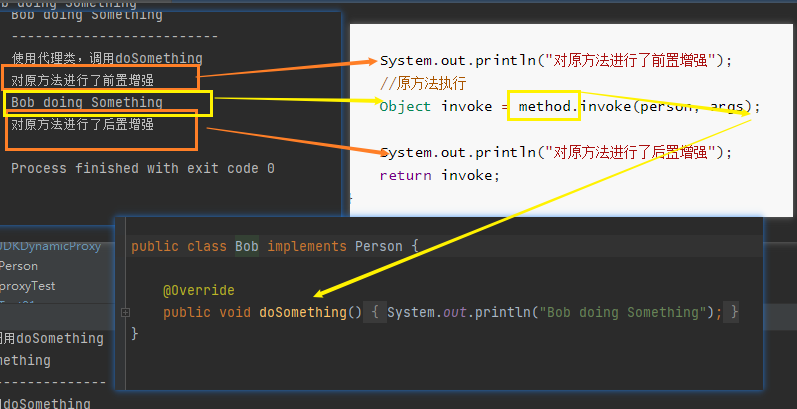
# 编写测试类
package com.gun.dynamicproxy;
public class proxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("不使用代理类,调用doSomething");
Person person = new Bob();
person.doSomething();
System.out.println("--------------------------");
System.out.println("使用代理类,调用doSomething");
// 获取代理对象
Person proxy = (Person) new JDKDynamicProxy(new Bob()).getTarget();
// 代理对象可以调用如何方法。
proxy.doSomething();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
这里proxy对象是动态生成的一个叫Bob的人【动态生成的】,这个人有各种行为【方法】,这里我们就是用了一个接口进行了统一规范。这个就是只有一个行为。那就是doSomething()。
当然也可以定义多个行为方法。
# cglib与jdk动态代理工厂
我要找房子,这不可能我亲力亲为吧。所以我要找个代理,于是我找了委托公司,委托公司给我动态的分配了一个代理,帮我去找房子。
# 第一步:创建找房子代理的接口
创建:IRentingHouse接口。
package designpattern.proxy.dynamicproxy;
/**
* 接口:租房
* jdk动态代理/cglib动态代理
*/
public interface IRentingHouse {
void rentHosue();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
这个接口描述的就是,委托公司分配给我的代理的具体描述信息。
这个代理:就会一个功能,找房子。
接口不能实例化,所以要去实现啰!
# 第二步:创建代理实现类
创建,实现类:IRentingHouse
package designpattern.proxy.dynamicproxy;
import designpattern.proxy.dynamicproxy.IRentingHouse;
/**
* 委托方(委托对象)
*/
public class RentingHouseImpl implements IRentingHouse {
@Override
public void rentHosue() {
System.out.println("我要租用一室一厅的房子");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
委托方是什么呢?
就比如:我叫你去打印资料。你没有去操作,而是委托你的朋友帮你打印资料,打印好的资料你朋友给了你,你在给了我。
我:在我看来就是你帮我打印的资料。我不知道你是找了一个委托对象帮你完成的。【我之蔽甚矣】
下满来看个打印代码的案例
package designpattern.delegation;
class RealPrinter { // the "delegate"
void print() {
System.out.print("something");
}
}
class Printer { // the "delegator"
// 委托对象
RealPrinter p = new RealPrinter(); // create the delegate
void print() {
// 委托对象的真实实现。
p.print(); // delegation
}
}
public class Main {
// to the outside world it looks like Printer actually prints.
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建打印器
Printer printer = new Printer();
// 打印器,调用打印方法帮我打印。
printer.print();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
在main方法中看是printer【Printer】对象帮你打印的,其实p【RealPrinter】对象帮你取打印的。
# 第三步:创建代理工厂类
代理工厂就是创建代理类对象的类。
package designpattern.proxy.dynamicproxy;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* @author lyp
* 代理对象工厂:生成代理对象的
*/
public class ProxyFactory {
private ProxyFactory(){
}
// 获取工厂实例,静态工厂设计模式
private static ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
public static ProxyFactory getInstance() {
return proxyFactory;
}
/**
* Jdk动态代理
* @param obj 委托对象
* @return 代理对象
*/
public Object getJdkProxy(Object obj) {
// 获取代理对象
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(obj.getClass().getClassLoader(), obj.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
// 写增强逻辑
System.out.println("中介(代理)收取服务费3000元");
// 调用原有业务逻辑
result = method.invoke(obj,args);
System.out.println("客户信息卖了3毛钱");
return result;
}
});
}
/**
* 使用cglib动态代理生成代理对象
* @param obj 委托对象 我找房子
* @return
*/
public Object getCglibProxy(Object obj) {
return Enhancer.create(obj.getClass(), new MethodInterceptor() {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
System.out.println("中介(代理)收取服务费3000元");
result = method.invoke(obj,objects);
System.out.println("客户信息卖了3毛钱");
return result;
}
});
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
# jdk动态代理的测试用例
package designpattern.proxy.dynamicproxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* @author lyp
*/
public class JdkProxy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//
IRentingHouse rentingHouse = new RentingHouseImpl(); // 委托对象---委托方
// 从代理对象工厂获取代理对象
//1、 获取工厂对象 ProxyFactory.getInstance() -》 ProxyFactory
//2、ProxyFactory对象的方法,获取 rentingHouse这个委托对象的 动态代理对象。
IRentingHouse jdkProxy = (IRentingHouse) ProxyFactory.getInstance().getJdkProxy(rentingHouse);
// 动态代理实例对象 调用它的方法。
jdkProxy.rentHosue();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
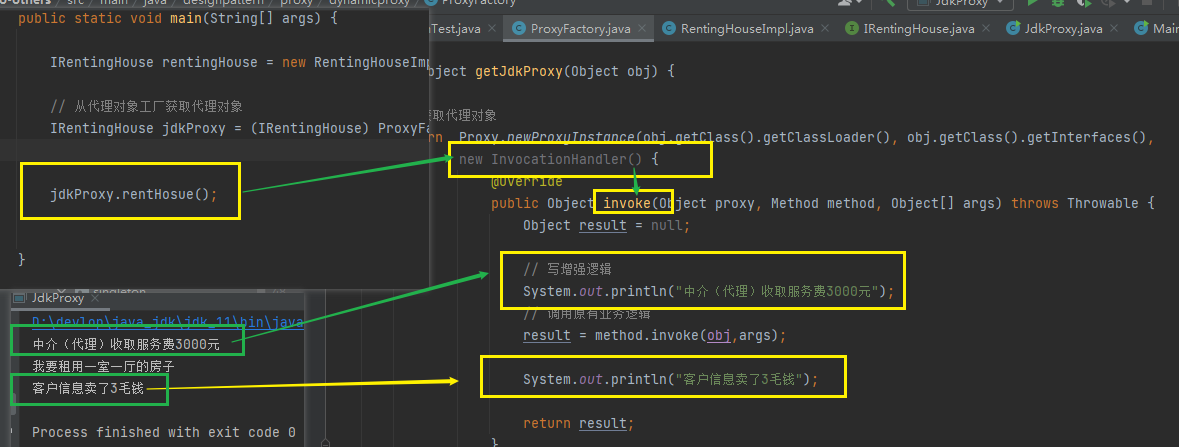
小结Proxy类的静态方法创建的动态代理类的实例有以下特点
每一个动态代理类实例都和一个InvocationHandler实例关联
Proxy的静态方法。getInvocationHandler(Object proxy)
参数:指定那个代理类实例对象。
返回值:返回一个与参数proxy指定对象关联的InvocationHandler对象。
InvocationHandler接口:为方法调用接口。作用:可以调用任一方法的invoke()方法进行执行。
# cglib动态代理的测试用例
使用cglib前要导入相关maven坐标
<!--引入cglib依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>2.1_2</version>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
6
package designpattern.proxy.dynamicproxy;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author liyupeng
*/
public class CglibProxy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RentingHouseImpl rentingHouse = new RentingHouseImpl(); // 委托对象
System.out.println(rentingHouse.getClass());
// 获取rentingHouse对象的代理对象,
// Enhancer类似于JDK动态代理中的Proxy
// 通过实现接口MethodInterceptor能够对各个方法进行拦截增强,类似于JDK动态代理中的InvocationHandler
// 使用工厂来获取代理对象
RentingHouseImpl cglibProxy = (RentingHouseImpl) ProxyFactory.getInstance().getCglibProxy(rentingHouse);
cglibProxy.rentHosue();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
cglib与jdk代理原来相同,底层实现不同。
我们主要怎么用jdk动态代理获取实现找房子接口类的动态代理类的实例。
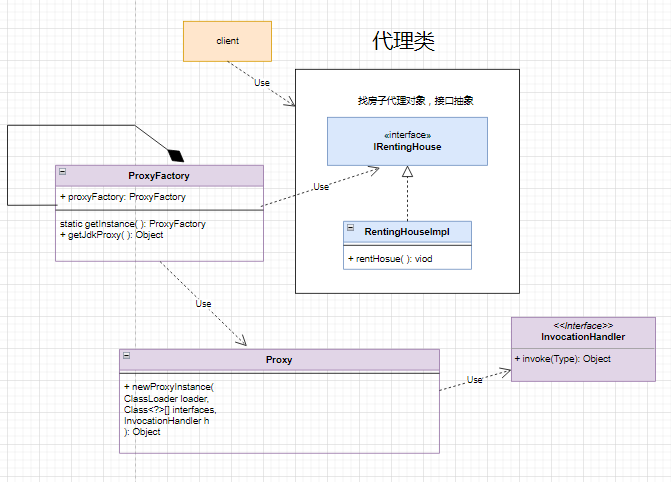
# JDK动态代理的UML图
客户端实例:
/**
* @author lyp
*/
public class JdkProxy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//
IRentingHouse rentingHouse = new RentingHouseImpl(); // 委托对象---委托方
// 从代理对象工厂获取代理对象
//1、 获取工厂对象 ProxyFactory.getInstance() -》 ProxyFactory
//2、ProxyFactory对象的方法,获取 rentingHouse这个委托对象的 动态代理对象。
IRentingHouse jdkProxy = (IRentingHouse) ProxyFactory.getInstance().getJdkProxy(rentingHouse);
// 动态代理实例对象 调用它的方法。
jdkProxy.rentHosue();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
- 先创建了找房代理对象的实例rentingHouse。
- 然后创建了一个动态代理类实例。【也就是你需要什么代理实例,把你描述的代理实例对象给工厂】
- 工厂返回的动态代理实例最后,这个实例对象调用了rentHosue()方法。【底层是JDK动态代理的实现】
# 手撸动态代理
# 分析
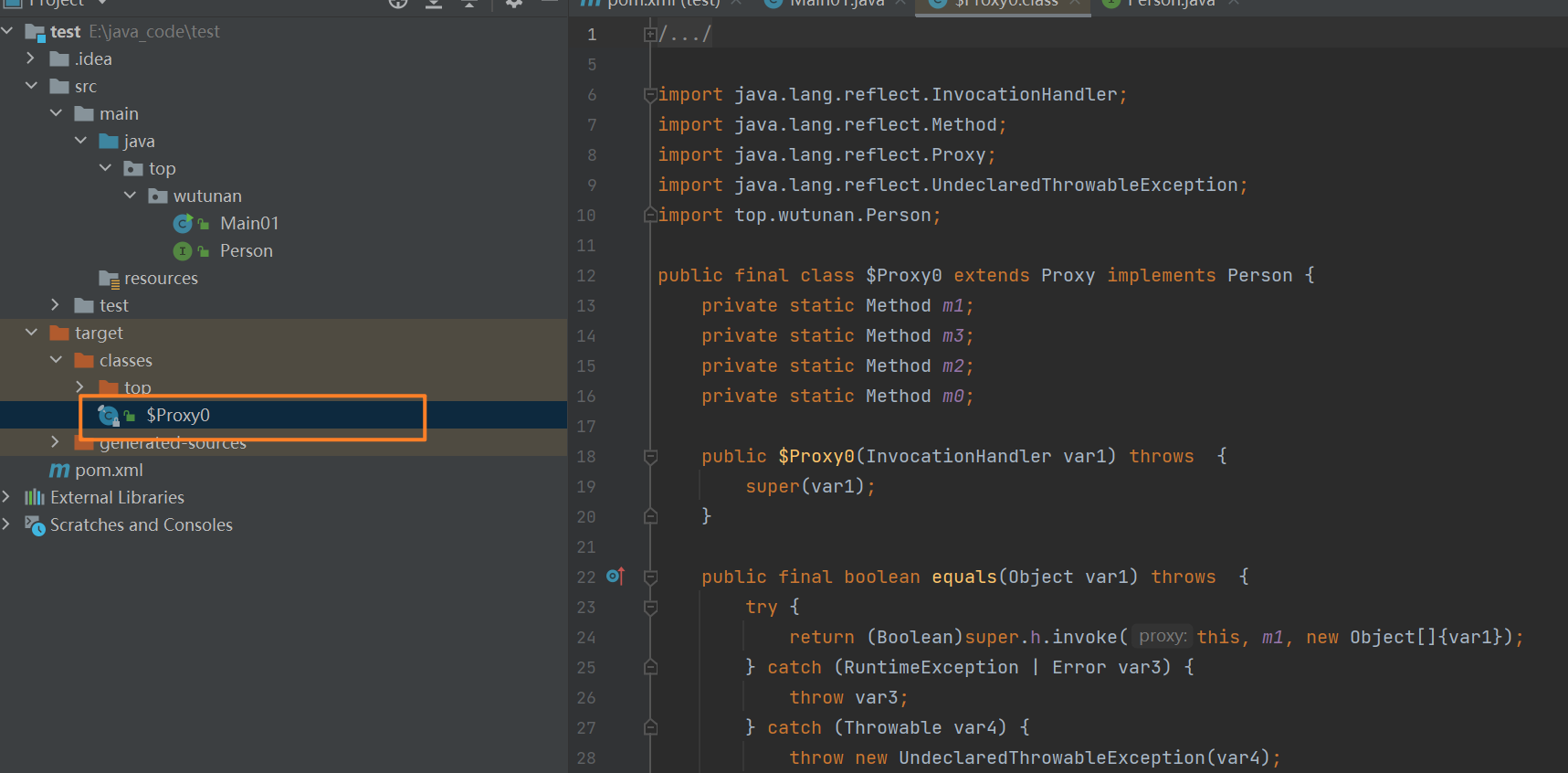
- 生成代理对象的字节码文件【java-jdk8】
package top.wutunan;
import sun.misc.ProxyGenerator;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.net.URL;
/**
* @Description
* @Author wutunan
* @Date 2024/5/5
*/
public class Main01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/**
* Object proxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(person.getClass().getClassLoader(),
* person.getClass().getInterfaces(),
* new Handler(person));
*
*
* proxyInstance 产生代理对象
*/
URL resource = Main01.class.getClass().getResource("/");
System.out.println(resource);
// JDk产生的字节码--class文件
// 参数一:直接码类名
// 代理对象的源码
byte[] bts = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass("$Proxy0", new Class[]{Person.class});
// 字节码文件输出
// 在target目录下产生class文件
File file = new File(resource.getPath(), "$Proxy0.class");
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
fos.write(bts);
fos.flush();
fos.close();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
运行结果
package top.wutunan;
/**
* 接口
*/
public interface Person {
public void doSomething();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
- 输出的结果
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException;
import top.wutunan.Person;
public final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements Person {
private static Method m1;
private static Method m3;
private static Method m2;
private static Method m0;
public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler var1) throws {
super(var1);
}
public final boolean equals(Object var1) throws {
try {
return (Boolean)super.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[]{var1});
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var3) {
throw var3;
} catch (Throwable var4) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var4);
}
}
public final void doSomething() throws {
try {
super.h.invoke(this, m3, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
public final String toString() throws {
try {
return (String)super.h.invoke(this, m2, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
public final int hashCode() throws {
try {
return (Integer)super.h.invoke(this, m0, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
static {
try {
m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", Class.forName("java.lang.Object"));
m3 = Class.forName("top.wutunan.Person").getMethod("doSomething");
m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString");
m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode");
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var2) {
throw new NoSuchMethodError(var2.getMessage());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) {
throw new NoClassDefFoundError(var3.getMessage());
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
# 字节码进行简化
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException;
import top.wutunan.Person;
public final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements Person {
public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler var1) {
super(var1);
}
public final void doSomething() throws {
super.h.invoke(this, m3, (Object[])null);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
← 组装者设计模式
